Learning Outcomes
i. Define and explain the concept of oxidation state, a crucial tool for understanding electron transfer in redox reactions.
ii. Assign oxidation states to elements in various compounds and molecules, including simple ionic and covalent compounds.
iii. Recognize the significance of oxidation states in identifying oxidizing and reducing agents in redox reactions.
iv. Apply the concept of oxidation states to balance redox equations and analyze the flow of electrons during chemical transformations.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of chemistry, where atoms engage in a silent dance of electron exchange, oxidation states emerge as a guiding light, illuminating the path of electrons and their transformations. This lesson will unveil the concept of oxidation state, empowering you to track the electrons' journey through chemical reactions and appreciate its significance in understanding the language of redox processes.
i. Defining Oxidation State: A Measure of Electron Gain or Loss
Oxidation state, also known as oxidation number, represents the hypothetical charge an atom would possess if all electrons were shared equally between its atoms in a molecule or compound. It provides a valuable tool for tracking electron transfers in redox reactions, revealing the gain or loss of electrons by individual atoms.
ii. Assigning Oxidation States: A Matter of Convention and Rules
Assigning oxidation states follows a set of conventions and rules:
- Elements in their free state or uncombined form have an oxidation state of zero.
- In ionic compounds, the oxidation state of an element is equal to its charge.
- In covalent compounds, the oxidation state of an element is determined by the electron distribution around it.
Examples of Oxidation States:
- Sodium (Na) in sodium chloride (NaCl): +1 oxidation state
- Oxygen (O) in water (H2O): -2 oxidation state
- Carbon (C) in methane (CH4): -4 oxidation state
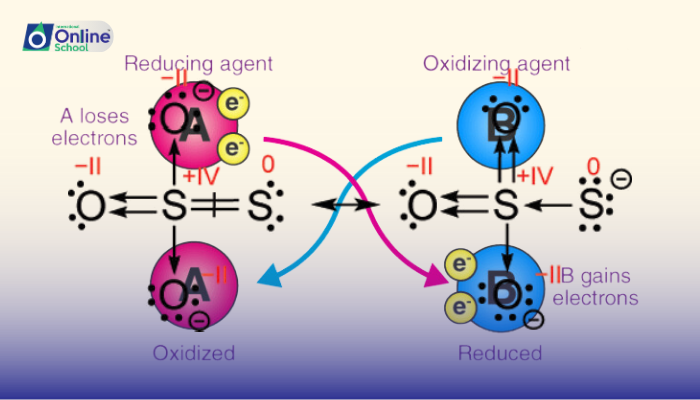
iii.Significance of Oxidation States: Unveiling Electron Flow
Oxidation states play a pivotal role in identifying oxidizing and reducing agents in redox reactions. The species that loses electrons and increases its oxidation state undergoes oxidation and acts as the reducing agent, while the species that gains electrons and decreases its oxidation state undergoes reduction and acts as the oxidizing agent.
iv. Balancing Redox Equations: A Matter of Electron Accounting
Balancing redox equations requires a careful accounting of electron transfers. By ensuring that the number of electrons lost by the reducing agent equals the number gained by the oxidizing agent and that the sum of oxidation states on both sides of the equation remains equal, we achieve a balanced representation of the electron exchange process.
Oxidation state, a fundamental concept in chemistry, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the intricate dance of electrons in redox reactions. By comprehending oxidation states, we gain insights into the gain or loss of electrons by individual atoms, enabling us to identify oxidizing and reducing agents, balance redox equations, and appreciate the language of chemical transformations.